Reporting implies that some changes are to be made to the original statement. These changes include modifications to pronouns, time adverbials and verb tenses. All of them are referred to as backshift.
Depending on the idea of the statement, we have or don't have to use backshit.
1. Obligatory backshift
If we don’t believe that the direct speech statement is true any longer, we must use backshift.
I’ve just spoken with him. He said he is going to be late as he is still at work. (Still true)
He said he was going to make a proposal but they broke up the previous month. (No longer true).
2. No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often occurs when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in the original statement:
He told me his friend works for a German company. (It is still true that his friend works for a German company.)
They promised they’ll help you. (Their promise applies to the future.)
3. Optional backshift
We use backshift when it is logical. For instance, if Mark said "I am hungry" two minutes ago and we are now telling his mum about it, we might not use backshift (because Mark is still hungry): Mark just said that he is hungry.
But if Mark said "I am hungry" yesterday and we are now telling his mum about it, it is better to use backshift: Yesterday, Mark said that he was hungry.
We usually don’t change the verb tense when:
1) the reported verb expresses a fact or a situation that is not going to change
They explained that these changes are essential according to the new law.
She told him that caring for other people makes every person better.
2) the verb comes after a time conjunction (when, after, etc.)
She said that she had started her career after she had left school.
They told us they got married when they had graduated from the university.
3) the action we are reporting is still happening or is going to happen
“I am looking after my neighbours’ dog while they are on holiday”. – She said she is looking after her neighbours’ dog while they are on holiday.
“There are lots of homeless animals everywhere.” – He said there are lots of stray animals everywhere.
However, we must remember that in all these examples above, the changes are optional, so it is possible and correct to change the verb tense.
● Here are some examples of common verb tenses and modals:
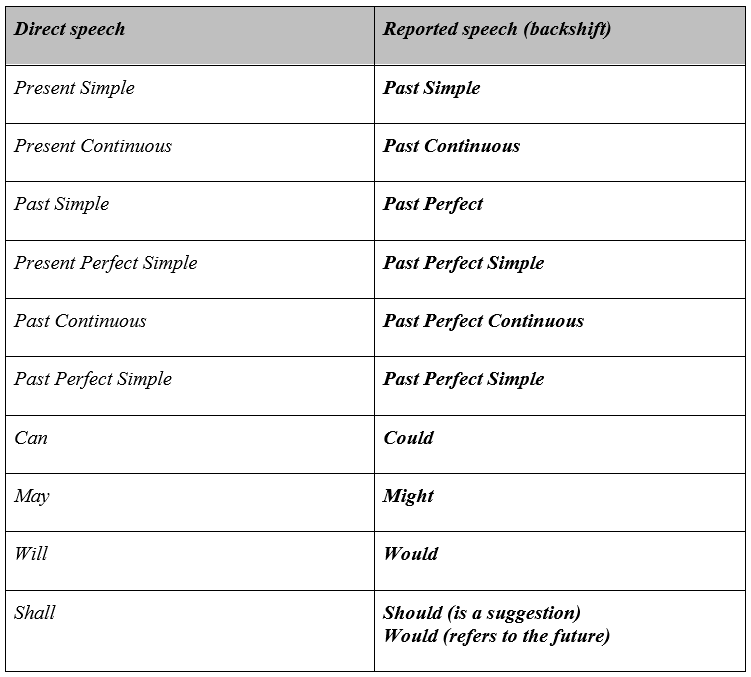
However, we don’t use backshift with modal verbs such as could, might, would, needn’t, ought to, should, must and had to.
You should make an appointment. – She said I should make an appointment.
You must listen to me. – She said that I must listen to her.
● Here are some examples of demonstratives, adverbs, and adverbial expressions:
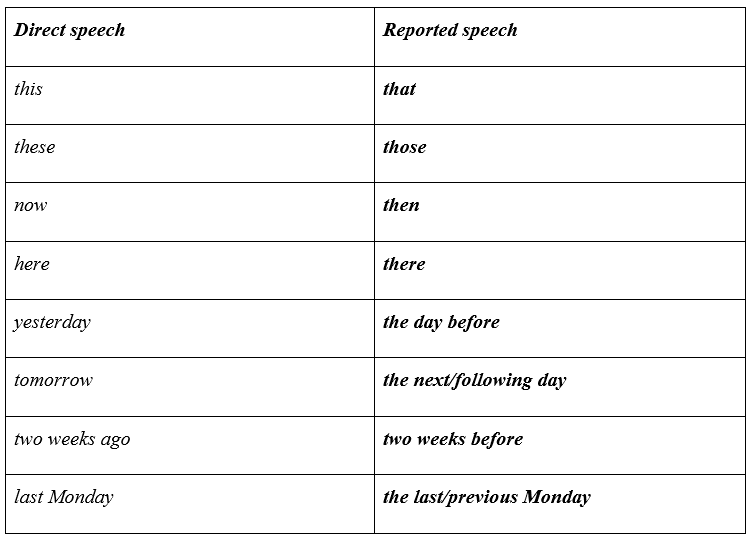
I will visit you tomorrow. - She said she would visit me the following day.
I lost my phone yesterday. - He said he had lost his phone the day before.
However, we don’t change the time and place references if the statement is reported on the same day or at the same place.
I will come here again at 5 p.m. tomorrow. – She said she will/would come here again at 5 p.m tomorrow.
● We can report somebody's words using reporting nouns as well as reporting verbs. These are more common in writing than speaking, and are usually quite formal. The reported clause after a reporting noun is usually a that-clause.
His remark that we hadn’t worked hard enough upset everyone.
Mark’s claim that he was ignored by everyone is hard to believe.
Here are some common reporting nouns: announcement, complaint, explanation, news, statement, response, criticism, claim, threat, answer, demand, offer, suggestion, denial, promise, admission, argument, comment, forecast, assertion, allegation, complaint, remark, warning, excuse, etc.